Upon placing a bet, your slot machine will 'spin the wheels', print the outcome, the payout and the current player's balance. Before the game begins the player will be prompted to enter the amount of currency (s)he has available to play on the slot machine. The slot machine always starts with 1,000 unites of currency. The following Visual Basic project contains the source code and Visual Basic examples used for slot machine game. This game includes a graphical slot machine that is created entirely by VB graphics methods such as Circle and Line.
- How To Make A Slot Machine In Visual Basic C++
- How To Make A Slot Machine In Visual Basic Java
- How To Create A Slot Machine In Visual Basic
I was bored and that can be a dangerous thing. Like doodling on the phone book while you are talking on the phone, I doodle code while answering questions on DIC. Yeah, it means I have no life and yes it means I was born a coder. During this little doodle I decided to make a slot machine. But not your standard slot machine per say, but one designed a little bit more like the real thing. Sure it could have been done a little more simpler and not even using a Wheel class at all, but what fun is that? In this entry I show the creation of a slot machine from a bit more of a mechanical aspect than a purely computerized one. It should provide a small sampling of classes and how they can represent real life machines. We cover it all right here on the Programming Underground!
So as I have already said, this little project was just something to play around with. It turned out kinda nice, so I thought I would share it. But what did I mean about it being mechanical in nature? Well, if you have ever played a real slot machine, not the digital ones they have in casinos now, you would see a metal case with a series of wheels. Typically it would be three wheels with pictures on them. When you put your money in and pull the handle the wheels would be set into motion. They would spin and then the first wheel would stop, followed by the second and then the third. After they have all stopped, the winnings are determined and you are paid out in coinage or credits.
I thought, why not be a bit mechanical in this slot machine design and create the wheels as a class called 'Wheel' and give it the ability to spin independently of the other wheels? Have the wheel keep track of which picture (or in our case number) is flying by and report the results to the actual slot machine class. I could have done this mechanism without the need of a wheel at all and instead load up an array and have it randomly pick a number from the wheel. Little slimmer, little more efficient but wouldn't show much programming theory.
What do we gain by recreating these Wheel classes and spinning them independently? Well, you gain a slight bit of flexibility. Independently we are able to control the speed of the spinning if we wanted to, we are able to grasp the idea of the wheel as a concept in our mind and manipulate it. We could easily built in features like if the wheel lands on a certain number it will adjust itself. Like some slots in Vegas, if you land on lets say a rocket in the center line, the machine would see the rocket and correct the wheel to spin backwards 1 spot (in the direction of the rocket as if the rocket was controlling the wheel). We could spin one wheel one way and another wheel another. We could inherit from that wheel and create a specialized wheel that does a slew of new different behaviors. All encapsulated into one solid object making the actual Machine class oblivious to the trickery of the wheel itself… encapsulation at its finest!
The machine class we create will contain 3 pointers. Each to one of the wheels. The machine itself will be in charge of a few different tasks. Taking money, issuing and removing credits, determining when to spin, telling each of the wheels to spin and checking our winnings based on some chart we create. It has enough on its plate than worrying about the wheels and reading their values.
So lets start with our Wheel class and its declaration/implementation…
wheel.h
As you can see the wheel itself is not a difficult concept to envision. The bulk of the work is in the read() method. Here we simply read the values from our internal array of integers (the values on the wheel) and return those values as an array of the three integers… representing the visible column. This column will then be loaded into our 2-Dimensional Array back in the Machine class. The 2D array represents the view or screen by which the user sees the results. Remember that the user never gets to see the entire wheel. Only the 3 consecutive values on the face of the wheel.
Here is how it may look in the real world. We have our machine with the three wheels and our 2D array called 'Screen' which acts as our viewing window. Each wheel will report its values and those values will be put into the screen…
Below is our machine class…
machine.h
This looks like a lot of code but really it is not if you look at each function. Most of them are very very simple to understand. We have a spin method which essentially spins each of the wheels, reads their values back from the Wheel class into a pointer (representing each column), then they are loaded into the 2D array one column at a time (our view screen), printed for the user to see the results and lastly the winnings are checked. The checkwinnings() method determines which rows to check based on the amount of the bet. If they chose 1 line, it checks for winning combinations on the middle row only. If they choose 2 lines, it checks the middle and top lines, 3 line bet checks all three horizontal rows, 4 line bet checks the first diagonal as well and 5 line bet checks both diagonals in addition to the lines.

How does it check the lines? Well each line is given to the checkline() helper function which compares the 3 values of the line against an enumerated type of various symbols. Here we are just assigning a symbol against each numbered value to help the programmer determine which numbers correspond to which winning combos. For instance, luckyseven represents the number 3 in the enumeration. So if it runs across a line with 3 number 3s, then it knows it hit the grand jackpot and credits the player 1000. This method makes things easy because if we ever wanted to change the win patterns later, we could change the enum and checkline method to do so. We could also build in multiple types of symbols and even let the user choose what slot machine game they want to go by. It becomes very flexible and is a testament to great design!
Lastly we can put some tests together just to show some the various aspects of how this thing works and how the programmer can use the classes…
slotmachine.cpp

This simply inserts a 5 dollar bill and a coin for good luck. Then bets 5 lines and spins. Despite the outcome we go and bet five lines again and spin once more. Hopefully we win something this time around! But either way, those are the classes for you and I hope you like them. As always, all code here on the Programming Underground is in the public domain and free for the taking (just don't cause a mess in isle 3, I am tired of running out there for cleanup). Thanks for stopping by and reading my blog. 🙂
[Lesson 32] << [Contents] >> [Lesson 34]
Although Visual Basic 2015 is a programming language designed for creating business and other industrial applications, it can be used to create animation. In the preceding lesson, we have actually learned how to create animation using the timer. In fact, the programs we have created in the previous lesson such as the stopwatch and the digital dice are animated programs.
We can create a continuously moving object using the timer. The motion can be from left to right or from top to bottom motion or diagonal.
33.1 Creating Motion
First, insert a picture box into the form. In the picture box properties window, select the image property and click to import an image file from your storage devices such as your hard drive, your pen drive or DVD drive. We have inserted an image of a bunch of grapes.Next, insert a Timer control into the form and set its Interval property to 100, which is equivalent to 0.1 seconds. Finally, add two buttons to the form, name one of them as AnimateBtn and the other one as StopBtn, and change to caption to Animate and Stop respectively.
We make use of the Left property of the picture box to create the motion. PictureBox.Left means the distance of the PictureBox from the left border of the Form. Now click on the Timer control and type in the following code:
In the code above, Me.Width represents the width of the Form. If the distance of the PictureBox from the left is less than the width of the Form, a value of 10 is added to the distance of the PictureBox from the left border each time the Timer tick, or every 0.1 seconds in this example. When the distance of the PictureBox from the left border is equal to the width of the form, the distance from the left border is set to 0, which move the PictureBox object to the left border and then move left again, thus creates an oscillating motion from left to right. We need to insert a button to stop motion. The code is:
To animate the PictureBox object, we insert a button and enter the following code:
The runtime interface
Figure 33.1
33.2 Creating a Graphical Dice
In preceding lessons, we have learned how to create graphics and draw objects on the form. Now we shall use the previous knowledge to create an animated graphical dice using the timer.
In this program, we need to insert a timer and set its interval to 100, which means the drawings will refresh every 0.1 seconds. Next, insert a picture box which is used as the surface of a dice. Finally, add a button and change its text to Roll. Under the Timer sub procedure, we create the Graphics object and the Pen object following the procedures we have learned in preceding lessons. Next, we use a Do loop and the Select Case structure to cycle through all six surfaces of the dice. To create six random cases, we use the syntax n = Int(6 * Rnd()) + 1. We can stop the loop by introducing a variable t and the loop until condition. The condition we set here is t>1000, you can use any figure you wish.
The code
The runtime interface is as shown in Figure 33.2
Figure 33.2
The Video Demo

So lets start with our Wheel class and its declaration/implementation…
wheel.h
As you can see the wheel itself is not a difficult concept to envision. The bulk of the work is in the read() method. Here we simply read the values from our internal array of integers (the values on the wheel) and return those values as an array of the three integers… representing the visible column. This column will then be loaded into our 2-Dimensional Array back in the Machine class. The 2D array represents the view or screen by which the user sees the results. Remember that the user never gets to see the entire wheel. Only the 3 consecutive values on the face of the wheel.
Here is how it may look in the real world. We have our machine with the three wheels and our 2D array called 'Screen' which acts as our viewing window. Each wheel will report its values and those values will be put into the screen…
Below is our machine class…
machine.h
This looks like a lot of code but really it is not if you look at each function. Most of them are very very simple to understand. We have a spin method which essentially spins each of the wheels, reads their values back from the Wheel class into a pointer (representing each column), then they are loaded into the 2D array one column at a time (our view screen), printed for the user to see the results and lastly the winnings are checked. The checkwinnings() method determines which rows to check based on the amount of the bet. If they chose 1 line, it checks for winning combinations on the middle row only. If they choose 2 lines, it checks the middle and top lines, 3 line bet checks all three horizontal rows, 4 line bet checks the first diagonal as well and 5 line bet checks both diagonals in addition to the lines.
How does it check the lines? Well each line is given to the checkline() helper function which compares the 3 values of the line against an enumerated type of various symbols. Here we are just assigning a symbol against each numbered value to help the programmer determine which numbers correspond to which winning combos. For instance, luckyseven represents the number 3 in the enumeration. So if it runs across a line with 3 number 3s, then it knows it hit the grand jackpot and credits the player 1000. This method makes things easy because if we ever wanted to change the win patterns later, we could change the enum and checkline method to do so. We could also build in multiple types of symbols and even let the user choose what slot machine game they want to go by. It becomes very flexible and is a testament to great design!
Lastly we can put some tests together just to show some the various aspects of how this thing works and how the programmer can use the classes…
slotmachine.cpp
This simply inserts a 5 dollar bill and a coin for good luck. Then bets 5 lines and spins. Despite the outcome we go and bet five lines again and spin once more. Hopefully we win something this time around! But either way, those are the classes for you and I hope you like them. As always, all code here on the Programming Underground is in the public domain and free for the taking (just don't cause a mess in isle 3, I am tired of running out there for cleanup). Thanks for stopping by and reading my blog. 🙂
[Lesson 32] << [Contents] >> [Lesson 34]
Although Visual Basic 2015 is a programming language designed for creating business and other industrial applications, it can be used to create animation. In the preceding lesson, we have actually learned how to create animation using the timer. In fact, the programs we have created in the previous lesson such as the stopwatch and the digital dice are animated programs.
We can create a continuously moving object using the timer. The motion can be from left to right or from top to bottom motion or diagonal.
33.1 Creating Motion
First, insert a picture box into the form. In the picture box properties window, select the image property and click to import an image file from your storage devices such as your hard drive, your pen drive or DVD drive. We have inserted an image of a bunch of grapes.Next, insert a Timer control into the form and set its Interval property to 100, which is equivalent to 0.1 seconds. Finally, add two buttons to the form, name one of them as AnimateBtn and the other one as StopBtn, and change to caption to Animate and Stop respectively.
We make use of the Left property of the picture box to create the motion. PictureBox.Left means the distance of the PictureBox from the left border of the Form. Now click on the Timer control and type in the following code:
In the code above, Me.Width represents the width of the Form. If the distance of the PictureBox from the left is less than the width of the Form, a value of 10 is added to the distance of the PictureBox from the left border each time the Timer tick, or every 0.1 seconds in this example. When the distance of the PictureBox from the left border is equal to the width of the form, the distance from the left border is set to 0, which move the PictureBox object to the left border and then move left again, thus creates an oscillating motion from left to right. We need to insert a button to stop motion. The code is:
To animate the PictureBox object, we insert a button and enter the following code:
The runtime interface
Figure 33.1
33.2 Creating a Graphical Dice
In preceding lessons, we have learned how to create graphics and draw objects on the form. Now we shall use the previous knowledge to create an animated graphical dice using the timer.
In this program, we need to insert a timer and set its interval to 100, which means the drawings will refresh every 0.1 seconds. Next, insert a picture box which is used as the surface of a dice. Finally, add a button and change its text to Roll. Under the Timer sub procedure, we create the Graphics object and the Pen object following the procedures we have learned in preceding lessons. Next, we use a Do loop and the Select Case structure to cycle through all six surfaces of the dice. To create six random cases, we use the syntax n = Int(6 * Rnd()) + 1. We can stop the loop by introducing a variable t and the loop until condition. The condition we set here is t>1000, you can use any figure you wish.
The code
The runtime interface is as shown in Figure 33.2
Figure 33.2
The Video Demo
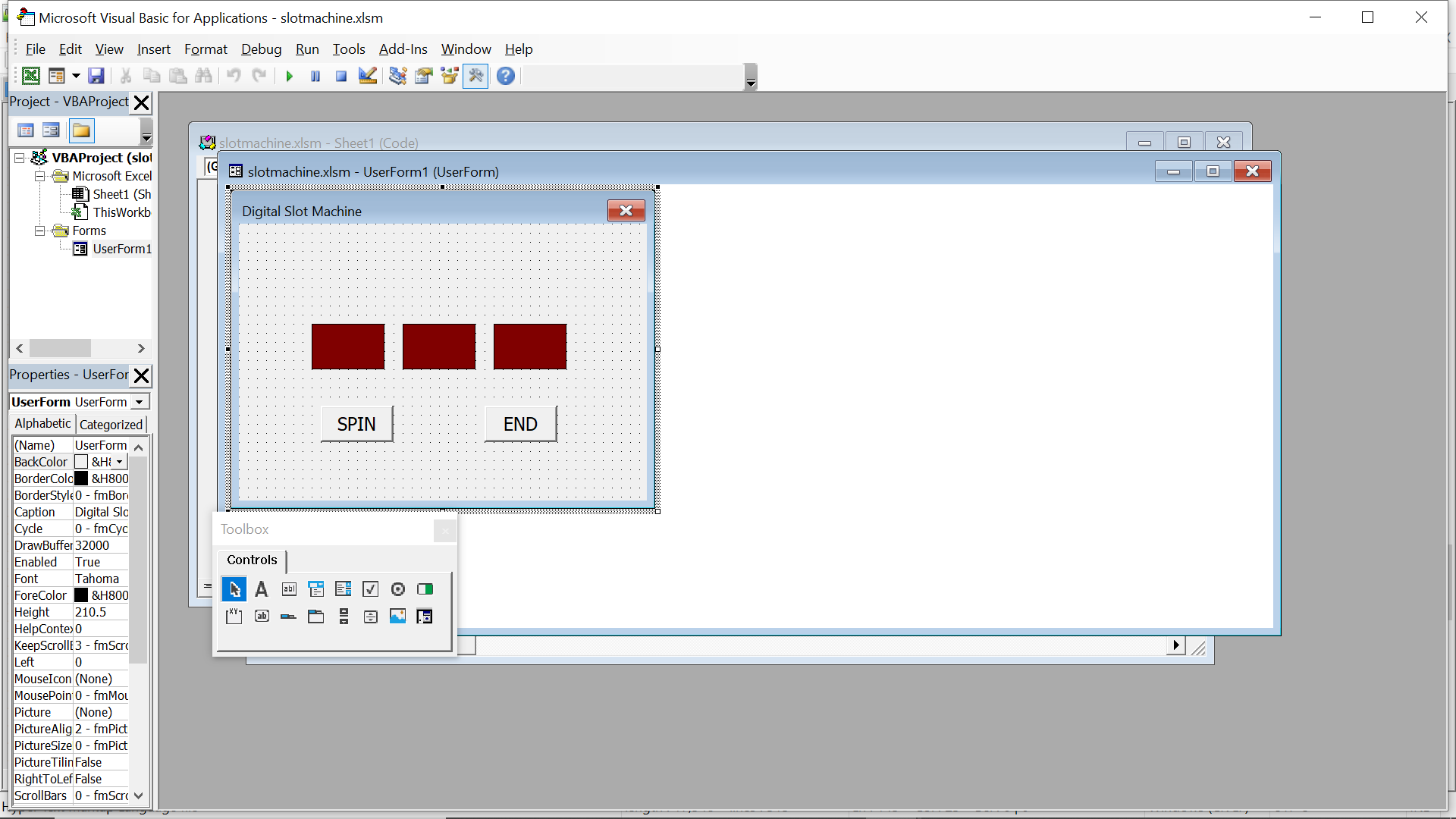
33.3 Creating a Slot Machine
In this program, we add three picture boxes, a timer, a button and a label. Set the timer interval to 10, which means the images will refresh every 0.01 second. In the code, we shall introduce four variables m, a, b and c, where m is used to stop the timer and a,b,c are used to generate random images using the syntax Int(1 + Rnd() * 3). To load the images, we use the following syntax:
PictureBox.Image = Image.FromFile(Path of the image file)
How To Make A Slot Machine In Visual Basic C++
We employ the If…Then structure to control the timer and the Select Case…..End Select structure to generate the random images. The label is used to display the message of the outcomes.
The Code
The run-time interface is shown in Figure 33.3
How To Make A Slot Machine In Visual Basic Java
Figure 33.3
How To Create A Slot Machine In Visual Basic
View the slot machine in action on the following video clip.
